
This question and its answers are locked because the question is off-topic but has historical significance.

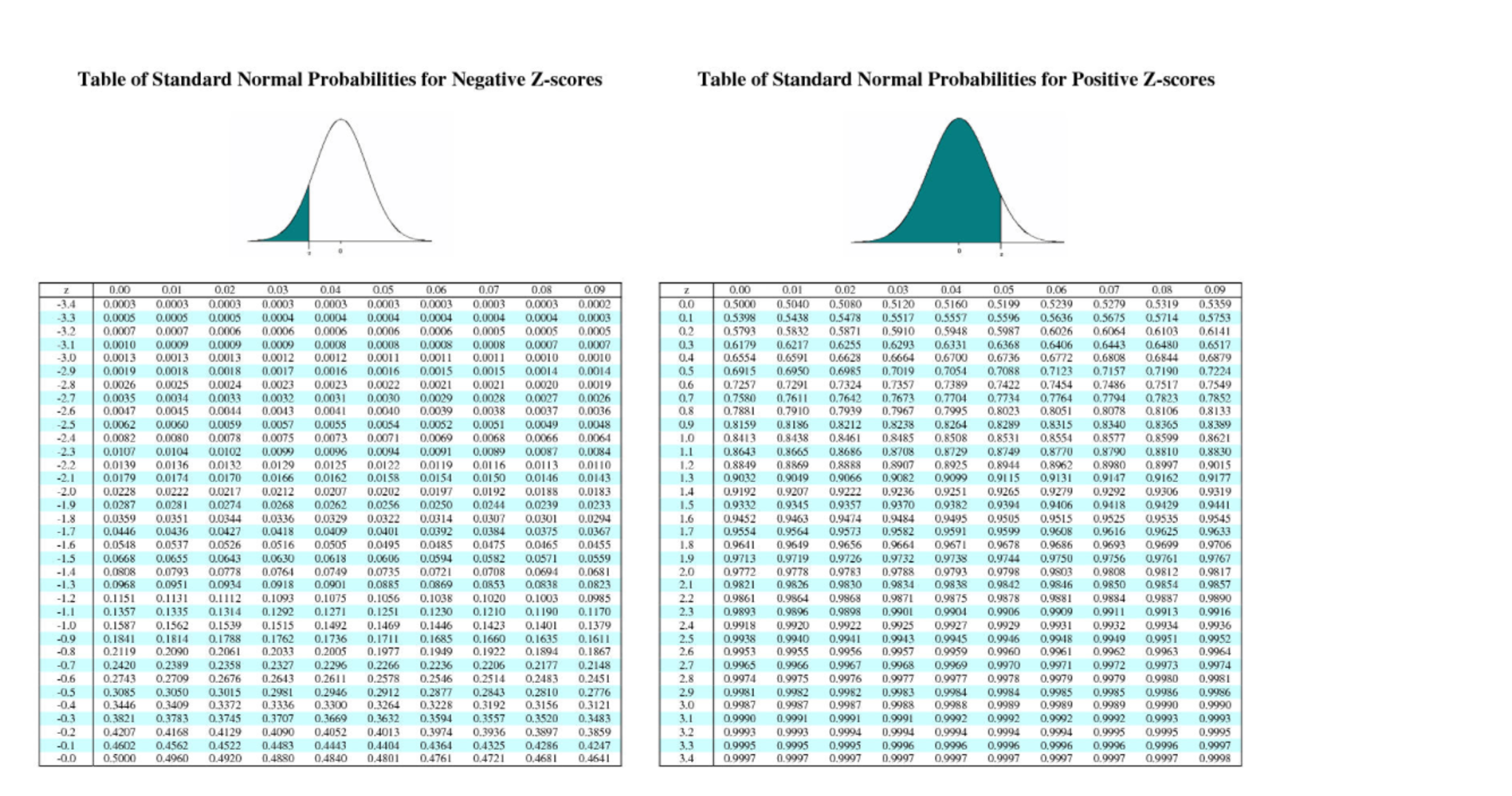
The table of z distribution is shown below. The CDF function of a Normal is calculated by translating the random variable to the Standard Normal, and then looking up a value from the precalculated 'Phi' function (Phi), which is the cumulative density function of the Standard Normal. Standard Normal Table latexpage Frequency Frequency is defined as the amount of times a value occurs. In R how do I referencelookup in the cdf of standard normal distribution table Ask Question Asked 10 years, 11 months ago. It is calculated as ( X – X bar) / sigma. The normal distribution is the most commonly used distributions in all of statistics. This file has been truncated.Z score is a measure of the distance in standard deviations of a sample from the mean. The values for negative values for z can be found by using the following equation because standard normal distribution is symmetrical: z z 1. It is also the upper one-sided N(0, 1) critical value and two-sided N(0, 1) critical value for the significance levels given in columns two and three, respectively. The fourth column is the N(0, 1) percentile for the percent given in column one. The table has values for (z) for nonnegative values for z (for the range 0 z 4.99). Cumulative Distribution Function (Normal Distribution) Provides the calculation to produce the Bell Curve significance value, the same output as the Excel Norm.Dist function, the calcs provided require just your Z-Score input. Table 2: Critical values (percentiles) for the standard normal distribution. To do the table approach, each normal CDF is converted to the standard normal CDF as follows: where is the z-score which is the ratio and is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution, which can be looked up from a table based on the z-score.

Rand(P::BiNormal) = let x = randn() x, P.ρ*x + P.ρ̄*randn() end The cumulative distribution function is given by: z ex dx z z ( ) < < 1 2 2 2. 2 2 1 2 1 ( ) x f x e Standard normal distribution table. A very complicated formula was used to find the areas under the curve. It is used to specify the distribution of.
-crop-1597154376382.png)
I have the bivariate case in : mschauer/GaussianDistributions.jl/blob/master/src/bivariate.jl # 100 Gauss Legendre points via "FastGaussQuadrature.jl"Ĭonst lnodes = Ĭonst lweights = īivariate standard normal distribution with correlation ρ Standard Normal Curve The normal or Gaussian curves are a family of bell-shaped curves named for the German mathematician and scientist Carl Friedrich Gauss. Normal distribution Also known as: Standard Normal Distribution Areas under the graph can be interpreted either as proportions or a probabilities. Cumulative Distribution Function states that the probability of the real-valued random variable X, will always take a value less than or equal to X.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
